EUR/USD explains the power amid uncertainty about the US economic view
- The euro/the US dollar rises to approximately 1.0850, as it weakens the US dollar amid accelerating concerns about American economic expectations.
- It is expected that the policies of US President Trump will slow the American economic growth.
- Centeno expects the European Central Bank to be almost an enlarged euro area outside the forest.
EUR/USD is circulating by about 1.0850 after recovering early losses in the North American session on Monday. The main currency pair is reinforced with the difficult US dollar (USD) to obtain a floor after a sharp decrease last week. The US dollar index (DXY), which tracks the value of Greenback for six main currencies, is being at risk near the lowest new level for four months at 103.50.
The US dollar expectations are not certain, as investors are increasingly concerned about how the policies of the President of the United States of America, Donald Trump, have been forming the economy. On Friday, the president’s comments indicated in an interview with Fox News that Trump’s policies should lead to short -term economic shocks.
Trump told “On Sunday morning.”
Recently, a large number of American data have indicated signs of economic slowdown, such as 15 -month low consumer confidence, an unexpected decrease in the manufacture of ISM new orders, and salary salary data slightly from February. The weak data of the merchants forced to raise the bets that support the Federal Reserve (Fed) to resume the policy pattern at the June meeting. The possibility of the Federal Reserve reduced interest rates in June to 82 % of 54 % per month, according to the CME Fedwatch tool.
Meanwhile, Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell continued to direct the approach to “waiting and learning interest rates due to the lack of clarity in the Trump tariff and tax policies. Powell said at an economic forum at Bath School at the University of Chicago on Friday” “uncertainty about the Trump administration policies and economic effects.”
Daily Digest Market Movers: EUR/USD shows the strength despite the euro deals with caution
- EUR/USD is still higher while EURO (EUR) is cautious against its main peers at the beginning of the week. The euro faces pressure, as the profit is reserved after its strong up -to -date move last week. The euro outperformed the performance as German leaders, including the new counselor Friedrich Mirz, agreed to extend the maximum borrowing or the so -called “debt brake” and the establishment of a 500 billion euro infrastructure fund to enhance defense spending and stimulate economic growth.
- Germany’s decision to stimulate the significant economic motivation of traders on the bets that support the European Central Bank (ECB) was forced to reduce interest rates twice this year, assuming that the effect may be inflationary in the euro area. Last week, the European Central Bank reduced the rate of 25 basis deposit facilities (BPS) to 2.5 %, but it did not commit a path for cash expansion in advance.
- Meanwhile, the comments of the policy maker from the European Central Bank and the ruler of Portugal Mario Sinino at a conference on Friday indicated that further cuts in interest rates are present in the pipeline. Sinino said that the euro area is on its way to “normalizing monetary policy.” Regarding inflation expectations, Centino said that inflation was “almost outside the forest” and has slowed down to “a level largely closer to our goal.”
- On the economic front, German industrial production data has grown for a month at a faster pace than expected in January. The industrial production of the euro area locomotive increased by 2 %, strongly of 1.5 % estimates. In December, it decreased by 1.5 %. Meanwhile, the confidence of the euro Cinxore investor is improving to -2.9 in March from -12.7 in February.
Technical Analysis: Euro/dollar remains above 200 days
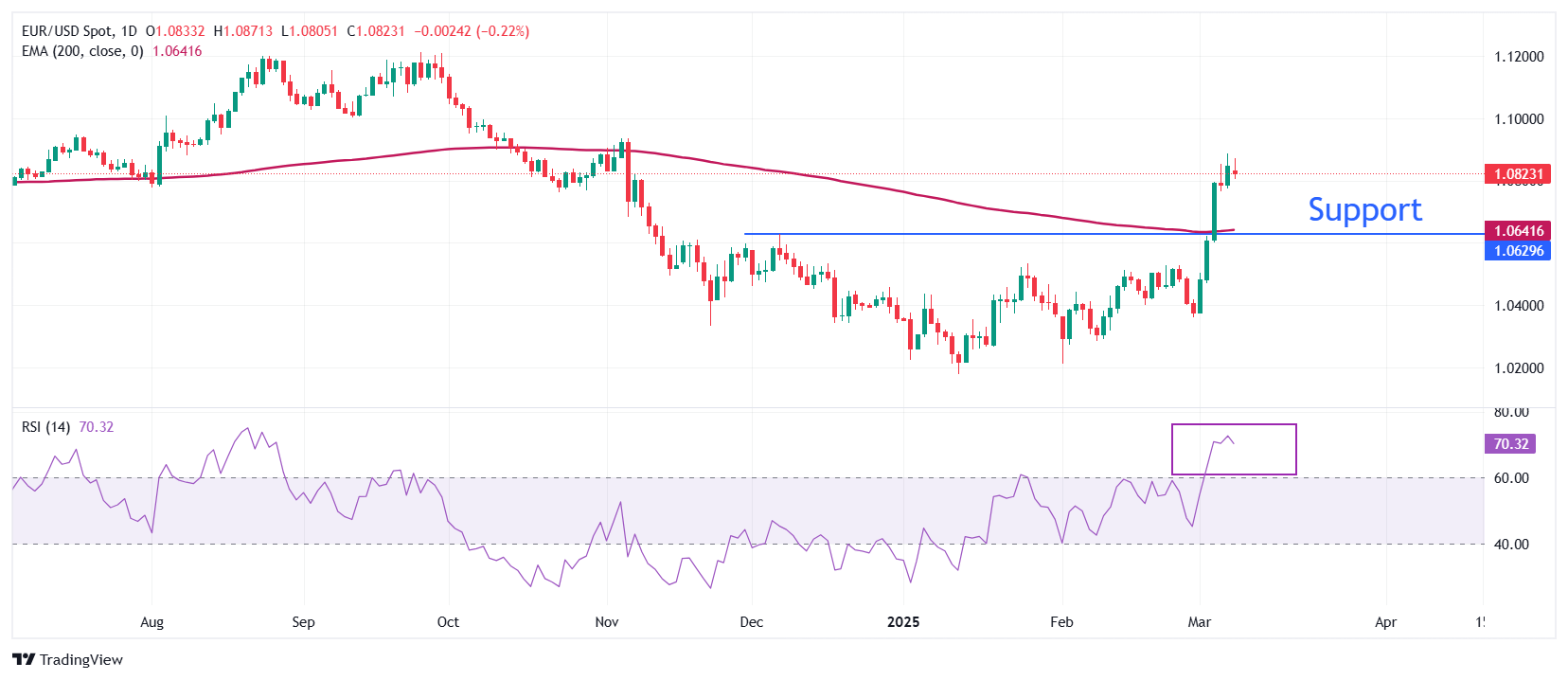
EUR/USD settles around 1.0850 after correction to nearly 1.0800 on Monday. The main currency pair was reinforced after a decisive outbreak of the highest level on December 6 of 1.0630 last week. Long -term expectations for the main currency pair as it exceeds the 200 -day SIA moving average (EMA), which trades around 1.0640.
The relative strength index jumps for 14 days (RSI) to approximately 70.00, indicating a strong upper momentum.
Looking down, the highest level on December 6 of 1.0630 will serve as the main support area of the husband. On the contrary, November 6 (Nove
Questions and answers in US dollars
The USD (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and a “reality” currency for a large number of other countries where there is a circulating alongside local notes. It is the most trading currency in the world, as it represents more than 88 % of the rotation of global foreign currencies, or on average $ 6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. In the aftermath of World War II, the United States took over the British pound the world reserves. For most of its history, the US dollar was backed by gold, even the Bretton Woods agreement in 1971 when the golden standard went.
The most important individual factor that affects the value of the US dollar is the monetary policy, which is formed by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Federal Reserve has two states: to achieve price stability (control of control) and enhance full employment. Its primary performance to achieve these two goals is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise very quickly and inflation is 2 % higher than the Federal Reserve goal, the Federal Reserve will raise rates, which helps the value of the dollar. When inflation decreases to less than 2 % or the unemployment rate is very high, the Federal Reserve may reduce interest rates, which weighs to green.
In maximum situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and quantitative mitigation (QE). QE is the process that the Federal Reserve increases significantly from the flow of credit in a suspended financial system. It is a measure of the non -standard policy used when the credit is dry because banks will not lend to each other (for fear of failing to pay the opposite end). It is the last resort when it is unlikely to achieve interest rates simply the necessary result. The Federal Reserve is the preferred to combat the credit crisis that occurred during the great financial crisis in 2008. It includes the printing of the Federal Reserve more dollars and their use to buy US government bonds mostly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to the weakest US dollar.
The quantitative tightening (QT) is the opposite process in which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not invest the manager from the bonds he holds in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.